HTML Forms
- An HTML form is used to collect user input. The user input is most often sent to a server for processing.
-
EX:
<form> <label for="name">First name:</label><br> <input type="text" id="name" name="name" value="Ahmed"><br> <label for="age">Age:</label><br> <input type="number" id="age" name="age" value="22"> </form> Result:
- The HTML
<form>element is used to create an HTML form for user input - The
<form>element is a container for different types of input elements, such as: text fields, checkboxes, radio buttons, submit buttons, etc. - The HTML
<input>element is the most used form element. - An
<input>element can be displayed in many ways, depending on the type attribute. -
EX:
Type Description <input type="text"> Displays a single-line text input field <input type="radio"> Displays a radio button (for selecting one of many choices) <input type="checkbox"> Displays a checkbox (for selecting zero or more of many choices) <input type="submit"> Displays a submit button (for submitting the form) <input type="button"> Displays a clickable button - The
<label>tag defines a label for many form elements. - The
<label>element is useful for screen-reader users, because the screen-reader will read out loud the label when the user focus on the input element.
The<label>element also help users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions (such as radio buttons or checkboxes) - because when the user clicks the text within the<label>element, it toggles the radio button/checkbox.
The for attribute of the<label>tag should be equal to the id attribute of the<input>
HTML Form Attributes
The Action Attribute
- The
actionattribute defines the action to be performed when the form is submitted. - Usually, the form data is sent to a file on the server when the user clicks on the submit button.
The Method Attribute
- The
methodattribute specifies the HTTP method to be used when submitting the form data. - The form-data can be sent as URL variables (with method="get") or as HTTP post transaction (with method="post").
-
Notes on GET:
- Appends the form data to the URL, in name/value pairs
- NEVER use GET to send sensitive data! (the submitted form data is visible in the URL!)
- The length of a URL is limited (2048 characters)
- Useful for form submissions where a user wants to bookmark the result
- GET is good for non-secure data, like query strings in Google
-
Notes on POST:
- Appends the form data inside the body of the HTTP request (the submitted form data is not shown in the URL)
- POST has no size limitations, and can be used to send large amounts of data.
- Form submissions with POST cannot be bookmarked
List of All form Attributes
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| accept-charset | Specifies the character encodings used for form submission |
| action | Specifies where to send the form-data when a form is submitted |
| autocomplete | Specifies whether a form should have autocomplete on or off |
| enctype | Specifies how the form-data should be encoded when submitting it to the
server (only for method="post"). when we submit a form with (input with type = file) we use enctype = "multipart/form-data". |
| method | Specifies the HTTP method to use when sending form-data |
| name | Specifies the name of the form |
| novalidate | Specifies that the form should not be validated when submitted |
| rel | Specifies the relationship between a linked resource and the current document |
| target | Specifies where to display the response that is received after submitting the form |
The HTML form Elements
The HTML form element can contain one or more of the following form elements:
-
<input> -
<label> -
<select> -
<textarea> -
<button> -
<fieldset> -
<legend> -
<datalist> -
<output> -
<option> -
<optgroup>
The select Element
- The select element defines a drop-down list.
-
EX:
<form> <label for="cars">Choose a car:</label> <select id="cars" name="cars"> <option value="volvo">Volvo</option> <option value="saab">Saab</option> <option value="fiat">Fiat</option> <option value="audi">Audi</option> </select> </form> -
Use the
sizeattribute in select element to specify the number of visible values.
<select id="cars" name="cars"size="3"></select> -
The
<option>elements defines an option that can be selected.
By default, the first item in the drop-down list is selected.
To define a pre-selected option, add theselectedattribute to the option:
<option value="fiat"selected>Fiat</option> -
Use the
multipleattribute to allow the user to select more than one value.
<select id="cars" name="cars" size="4"multiple></select>
The textarea Element
- The
<textarea>element defines a multi-line input field (a text area). -
EX:
<textareaname="message"rows="10"cols="30"></textarea> - The rows attribute specifies the visible number of lines in a text area.
- The cols attribute specifies the visible width of a text area.
The button Element
- The
<button>element defines a clickable button. -
EX:
<buttontype="button"onclick="alert('Hello World!')">Click </button>
HTML Form Elements
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <form> | Defines an HTML form for user input |
| <input> | Defines an input control |
| <textarea> | Defines a multiline input control (text area) |
| <label> | Defines a label for an <input> element |
| <fieldset> | Groups related elements in a form |
| <legend> | Defines a caption for a <fieldset> element |
| <select> | Defines a drop-down list |
| <optgroup> | Defines a group of related options in a drop-down list |
| <option> | Defines an option in a drop-down list |
| <button> | Defines a clickable button |
| <datalist>/td> | Specifies a list of pre-defined options for input controls |
| <output> | Defines the result of a calculation |
HTML Input Types
Here are the different input types you can use in HTML:
<input type="button"><input type="checkbox"><input type="color"><input type="date"><input type="datetime-local"><input type="email"><input type="file"><input type="hidden"><input type="image"><input type="month"><input type="number"><input type="password"><input type="radio"><input type="range"><input type="reset"><input type="search"><input type="submit"><input type="tel"><input type="text"><input type="time"><input type="url"><input type="week">
<input type="text"> |
defines a single-line text input field. | |
<input type="password"> |
defines a password field. | |
<input type="email"> |
is used for input fields that should contain an e-mail address. | |
<input type="file"> |
defines a file-select field and a "Browse" button for file uploads. | |
<input type="submit"> |
defines a button for submitting form data to a form-handler. | |
<input type="reset"> |
defines a reset button that will reset all form values to their default values. | |
<input type="Radio"> |
Radio buttons let a user select ONLY ONE of a limited number of choices. |
|
<input type="checkbox"> |
Checkboxes let a user select ZERO or MORE options of a limited number of choices. |
|
<input type="button"> |
defines a button. | |
<input type="color"> |
is used for input fields that should contain a color. | |
<input type="datetime-local"> |
specifies a date and time input field, with no time zone. | |
<input type="date"> |
is used for input fields that should contain a date. | |
| You can also use the min and max attributes to add restrictions to dates. | ||
<input type="Hidden"> |
|
|
<input type="number"> |
defines a numeric input field. | |
| You can also set restrictions on what numbers are accepted. | ||
<input type="range"> |
defines a control for entering a number whose exact value is not important (like a slider control). Default range is 0 to 100. However, you can set restrictions on what numbers are accepted with the min, max, and step attributes. | |
Input Restrictions
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| checked | Specifies that an input field should be pre-selected when the page loads (for type="checkbox" or type="radio") |
| disabled | Specifies that an input field should be disabled |
| max | Specifies the maximum value for an input field |
| maxlength | Specifies the maximum number of character for an input field |
| min | Specifies the minimum value for an input field |
| pattern | Specifies a regular expression to check the input value against |
| readonly | Specifies that an input field is read only (cannot be changed) |
| required | Specifies that an input field is required (must be filled out) |
| size | Specifies the width (in characters) of an input field |
| step | Specifies the legal number intervals for an input field |
| value | Specifies the default value for an input field |
HTML class Attribute
-
The HTML class attribute is used to specify a class for an HTML element.
EX:
<h2 class="className">This is h2</h2> -
Multiple HTML elements can share the same class.
EX:
<h2 class="class1Name">This is h2</h2> <h2 class="class2Name">This is h2</h2> -
The class attribute is often used to point to a class name in a style sheet. It can also be used by a JavaScript to access and manipulate elements with the specific class name.
EX:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> .name{ background-color: aliceblue; padding: 10px; } </style> </head> <body> <button onclick="myFunction()">Hide element</button> <h2 class="name">this h2 will be hiden when you click the button. </h2> <script> function myFunction() { var mainObject = document.getElementsByClassName("name"); mainObject[0].style.display = "none"; } </script> </body> </html>
HTML id Attribute
-
The HTML id attribute is used to specify a unique id for an HTML element.
EX:
<h2 id="idName">This is h2</h2> - The id attribute specifies a unique id for an HTML element. The value of the id attribute must be unique within the HTML document.
-
The id attribute is used to point to a specific style declaration in a style sheet. It is also used by JavaScript to access and manipulate the element with the specific id.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> .button{ background-color: aliceblue; padding: 15px; } #myHeader{ background-color: aliceblue; padding: 15px; } </style> </head> <body> <h1 id="myHeader">this h2 will be change when you click the button.</h1> <button onclick="displayResult()" class="button">Change text</button> <script> function displayResult() { document.getElementById("myHeader").innerHTML = "text Changed"; } </script> </body> </html> -
HTML bookmarks are used to allow readers to jump to specific parts of a webpage.
Bookmarks can be useful if your page is very long.
To use a bookmark, you must first create it, and then add a link to it.
Then, when the link is clicked, the page will scroll to the location with the bookmark.
EX:
<h2 id="C6">Chapter 6</h2> <a href="#C6">Jump to Chapter 6</a>
HTML && Css
- Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) is used to format the layout of a webpage.
-
CSS can be added to HTML documents in 3 ways:
- Inline - by using the
styleattribute inside HTML elements - Internal - by using a
<style>element in the<head>section - External - by using a
<link>element to link to an external CSS file
- Inline - by using the
-
Inline CSS
- An inline CSS is used to apply a unique style to a single HTML element.
-
EX:
<h1style="color:blue;">A Blue Heading</h1>
-
Internal CSS
- An internal CSS is used to define a style for a single HTML page.
- An internal CSS is defined in the
<head>section of an HTML page, within a<style>element. -
EX:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <style> body {background-color: powderblue;} .h1Element {color: blue;} #pElement {color: red;} </style> </head> <body> <h1 class="h1Element">This is a heading</h1> <p id="pElement">This is a paragraph.</p> </body> </html>
-
External CSS
- An external style sheet is used to define the style for many HTML pages.
- We will talk about it in detail in the next lessons
Semantic Elements in HTML
- A semantic element clearly describes its meaning to both the browser and the developer.
- Examples of non-semantic elements:
<div>and<span>- Tells nothing about its content. - Examples of semantic elements:
<form>,<table>, and<article>- Clearly defines its content.
Below is a list of some of the semantic elements in HTML.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| <section> | Defines a section in a document |
Examples of where a section element can be used:
|
|
| <article> | Defines independent, self-contained content |
Examples of where the article element can be used:
|
|
| <aside> | Defines content aside from the page content |
| <details> | Defines additional details that the user can view or hide |
| <figcaption> | Defines a caption for a <figure> element |
| <figure> | Specifies self-contained content, like illustrations, diagrams, photos, code listings, etc. |
| <header> | Specifies a header for a document or section |
A header element typically contains:
|
<footer> | Defines a footer for a document or section |
A footer element typically contains:
|
|
| <main> | Specifies the main content of a document |
| <mark> | Defines marked/highlighted text |
| <nav> | Defines navigation links |
| <summary> | Defines a visible heading for a <details> element |
| <time> | Defines a date/time |
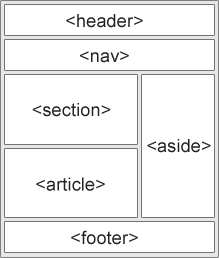
parts of a web page
- Many web sites contain HTML code like: <div id="nav"> <div class="header"> <div id="footer"> to indicate navigation, header, and footer.
-
In HTML there are some semantic elements that can be used to define different parts of a web page like
<article><aside><footer><header>main<nav><section>
Extra Sources
There are more lessons in that chapter but it's your turn to try to find and learn them and here are some examples:
- HTML Image Maps
- HTML Computer Code Elements
- HTML Symbols
- Using Emojis in HTML
- HTML Canvas Graphics
- HTML SVG Graphics
- Regular Expressions
- And more......
