Introduction To course
Welcome to the course, We are happy to be here and honored to work with you and we hope to be as you think and benefit you with everything new.
Master Code Team...
Course Content
🎴 Frontend Developer
You Will Learn Some of Techniques like :
- HTML5 & CSS
- JAVASCRIPT Fandumentals
- Responsive Web Design
- Learn Bootstrap
💻 Backend Developer
You Will Learn Some of Techniques like :
- MySQL & Databases
- PHP Fandumentals
- OOP
- MVC Structure
- Laravel Framework
🌐 General Topics
- Create Your Full-Stack Project
- Git & Github
- How to Upload Your Website On a Server
- How to Buy Servers & Domains
- Problem Solving and Searching Experience
- Freelancing
Skills To Learn
- search first before asking
- have a target and focus on it
- try to get alot of ideas
- please search on google before asking
- Never say I can't or that's impossible
Tools To Learn
- Text Editor [ Visual Studio Code || Atom ]
- Mobile Text Editor [ anWriter HTML editor || Acode ]
- Internet Browser [ Google Chrome || Firefox || Microsoft Edge ]
- Notes
How The Website Works ?
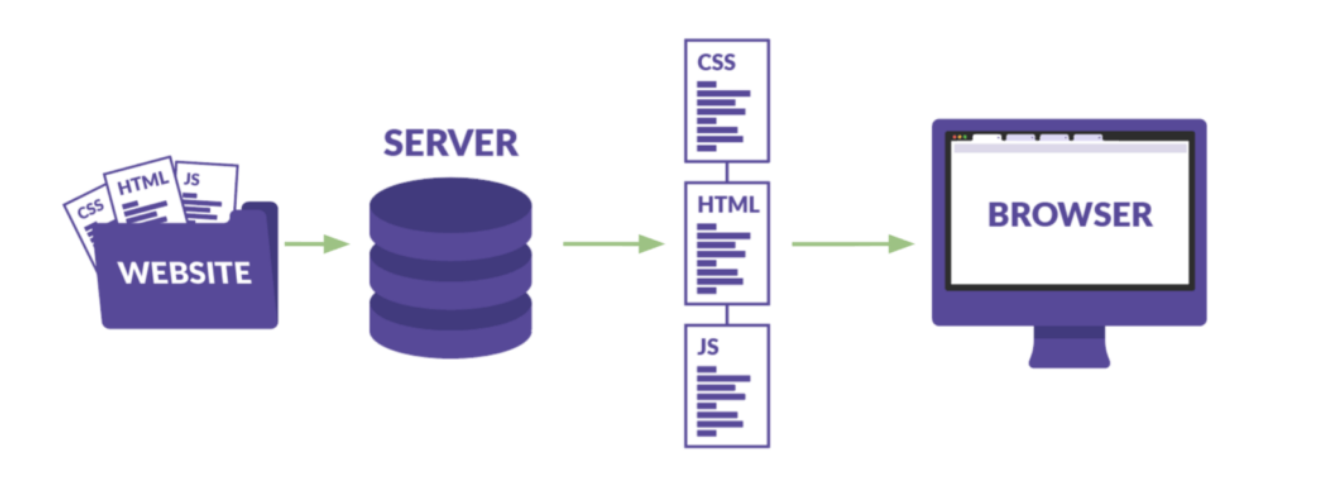
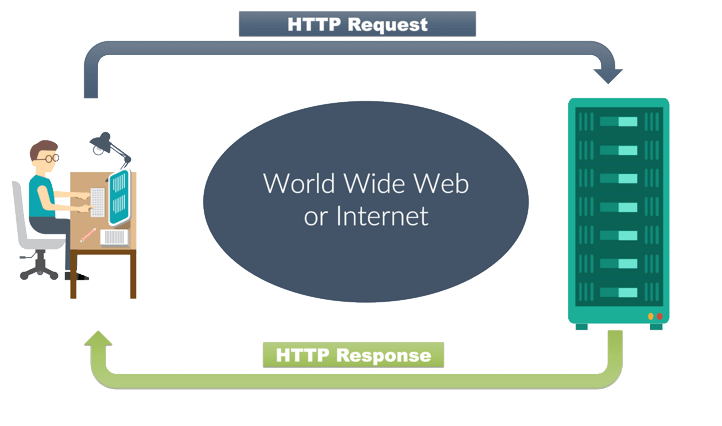
What is HTML?
- HTML stands for Hyper Text Markup Language
- HTML describes the structure of a Web page
- HTML elements tell the browser how to display the content
- HTML elements label pieces of content such as "this is a heading", "this is a paragraph", "this is a link", etc.....
A Simple HTML Document
HTML Versions
| Year | Version |
|---|---|
| 1989 | Tim Berners-Lee invented www |
| 1991 | Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML |
| 1993 | Dave Raggett drafted HTML+ |
| 1995 | HTML Working Group defined HTML 2.0 |
| 1997 | HTML 3.2 |
| 1999 | HTML 4.01 |
| 2000 | XHTML 1.0 |
| 2002 | XHTML 2.0 |
| 2008 | WHATWG HTML5 First Public Draft |
| 2012 | HTML5 |
| 2016 | HTML 5.1 |
| 2017 | HTML5.1 2nd Edition |
| 2017 | HTML5.2 |
Structural Layer
HTML stands for Hypertext Markup Language, you can basically use HTML to to build a webpage reason why is the “structural layer” in the picture. Since HTML consists of a head and body you can also add a variety of things that makeup the webpage. In HTML you can add tables, paragraphs of text,headlines, images, videos,links, and more.
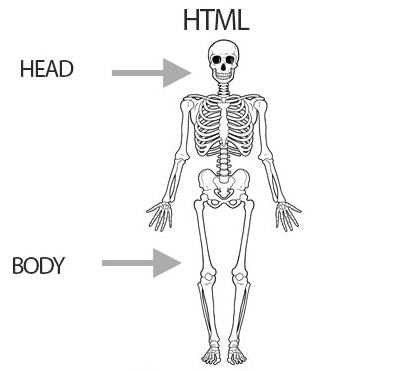
HTML Documents
- All HTML documents must start with a document type declaration : <!DOCTYPE html>.
- The HTML document itself begins with <html> and ends with </html>.
- The visible part of the HTML document is between <body> and </body>.
The <!DOCTYPE> Declaration
- The <!DOCTYPE> declaration represents the document type and version, and helps browsers to display web pages correctly.
- The <!DOCTYPE> declaration for HTML5 is: <!DOCTYPE html>.
- It must only appear once, at the top of the page (before any HTML tags).
-
Older HTML Documents
In older documents (HTML 4 or XHTML), the declaration is more complicated because the declaration must refer to a DTD (Document Type Definition).
HTML 4.01:
<!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
The Head Element
- The HTML <head> element is a container for the following elements: <title>, <style>, <meta>, <link>, <script>, and <base>.
- The <head> element is a container for metadata (data about data) and is placed between the <html> tag and the <body> tag.
- Metadata typically define the document title, character set, styles, scripts, and other meta information.
- The metadata will not be displayed on the page, but are used by browsers (how to display content or reload page), by search engines (keywords), and other web services.
Elements Of Head
HTML Elements
- The HTML element is everything from the start tag to the end tag: <tagname>Content goes here...</tagname>
- Examples of some HTML elements: <h1>This Is Header</h1>
HTML Headings
- HTML headings are defined with the <h1> to <h6> tags.
- <h1> defines the most important heading. <h6> defines the least important heading.
-
Heading 1
Heading 2
Heading 3
Heading 4
Heading 5
Heading 6
- Search engines use the headings to index the structure and content of your web pages.
- <h1> headings should be used for main headings, followed by <h2> headings, then the less important <h3>, and so on.
HTML Paragraphs
- The HTML <p> element defines a paragraph.
HTML Lists
- HTML lists allow web developers to group a set of related items in lists.
HTML Links
- HTML links are hyperlinks when click on a link and jump to another document.
- The HTML <a> tag defines a hyperlink.
- It has the following syntax: <a href="url">link text</a>
-
The target Attribute :
- By default, the linked page will be displayed in the current browser window. To change this, you must specify another target for the link.
- Example : <a href="https://www.Google.com/" target="_blank">Visit Google!</a>
-
The target attribute can have one of the following values:
- _self - Default. Opens the document in the same window/tab as it was clicked
- _blank - Opens the document in a new window or tab
- _parent - Opens the document in the parent frame
- _top - Opens the document in the full body of the window
-
Link to an Email Address
- Use mailto: inside the href attribute to create a link that opens the user's email program (to let them send a new email).
- Example : <a href="mailto:someone@example.com">Send email</a>
-
Create a Bookmark in HTML
- Bookmarks can be useful if a web page is very long.
- Example :
<h2 id="C6">Chapter 6</h2>
<a href="#C6">Jump to Chapter 6</a>
HTML Comment Tags
- You can add comments to your HTML source by using the following syntax:
<!-- Write your comments here --> . - With comments you can place notifications and reminders in your HTML code
- Comments are also great for debugging HTML, because you can comment out HTML lines of code, one at a time, to search for errors.
HTML Formatting Elements
- Formatting elements were designed to display special types of text:
- <b> - Bold text
- <strong> - Important text
- <i> - Italic text
- <em> - Emphasized text
- <mark> - Marked text
- <small> - Smaller text
- <del>
- Deleted text - <ins> - Inserted text
- <sub> - Subscript text
- <sup> - Superscript text
